RST is preparing a quotation, on a relevant cost basis, for a special order.
Which TWO of the following are relevant costs that should be included in the quotation?
A company is considering the use of Material V in a special order.
The material is used regularly and a sufficient quantity of the material is in inventory.
It could also be sold, at just below the current market price, to a local competitor.
What is the relevant cost of Material V to be used in the special contract?
XY can choose from four mutually exclusive projects. The projects will each last for one year and their net cash inflows will be determined by market conditions. The forecast net cash inflows for each of the possible outcomes are shown below.

If the company applies the maximax criterion the project chosen would be:
Assume that you have made profit calculations based on standard profit calculation methods and activity based costing methods.
In which ways will this information be beneficial to the management team?
Select all the true statements.
A clinic offers two types of procedure, A and B.
The clinic uses activity-based costing. The general facility overhead cost for next year is budgeted to be $8,601,600. The cost driver is the length of patient stay.
Additional data:

What is the general facility overhead cost for each Procedure B?
For a company that does not have any production resource limitations, what would be the correct sequence for budget preparation?

A company produces trays of pre-prepared meals that are sold to restaurants and food retailers. Three varieties of meals are sold: economy, premium and deluxe.


Calculate, for the original budget, the budgeted fixed overhead costs, the budgeted variable overhead cost per tray and the budgeted total overheads costs.
The labour requirement for a special contract is 250 skilled labour hours paid at $10 per hour and 750 semi-skilled labour hours paid at $8 per hour.
At present, skilled labour is fully utilised on other contracts which generate a $12 contribution per hour, after charging labour costs. Additional skilled labour is unavailable in the short term.
There is a surplus of 1,200 semi-skilled hours over the period of the contract but the firm has a policy of no redundancies.
The relevant cost of labour for the special contract is:
A company’s budget for the next period shows that it would breakeven at sales revenue of $800,000 and fixed costs of $320,000.
The sales revenue needed to achieve a profit of $200,000 in the next period would be:
RFT, an engineering company, has been asked to provide a quotation for a contract to build a new engine. The potential customer is not a current customer of RFT, but the directors of RFT are keen to try and win the contract as they believe that this may lead to more contracts in the future. As a result, they intend pricing the contract using relevant costs. The following information has been obtained from a two-hour meeting that the Production Director of RFT had with the potential customer. The Production Director is paid an annual salary equivalent to $1,200 per 8-hour day. 110 square meters of material A will be required. This is a material that is regularly used by RFT and there are 200 square meters currently in inventory. These were bought at a cost of $12 per square meter. They have a resale value of $10.50 per square meter and their current replacement cost is $12.50 per square meter. 30 liters of material B will be required. This material will have to be purchased for the contract because it is not otherwise used by RFT. The minimum order quantity from the supplier is 40 liters at a cost of $9 per liter. RFT does not expect to have any use for any of this material that remains after this contract is completed. 60 components will be required. These will be purchased from HY. The purchase price is $50 per component. A total of 235 direct labour hours will be required. The current wage rate for the appropriate grade of direct labour is $11 per hour. Currently RFT has 75 direct labour hours of spare capacity at this grade that is being paid under a guaranteed wage agreement. The additional hours would need to be obtained by either (i) overtime at a total cost of $14 per hour; or (ii) recruiting temporary staff at a cost of $12 per hour. However, if temporary staff are used they will not be as experienced as RFT’s existing workers and will require 10 hours supervision by an existing supervisor who would be paid overtime at a cost of $18 per hour for this work. 25 machine hours will be required. The machine to be used is already leased for a weekly leasing cost of $600. It has a capacity of 40 hours per week. The machine has sufficient available capacity for the contract to be completed. The variable running cost of the machine is $7 per hour. The company absorbs its fixed overhead costs using an absorption rate of $20 per direct labour hour.
Select ALL the true statements.
Two products being produced by a company require the same material which is limited to 2,600 kgs.
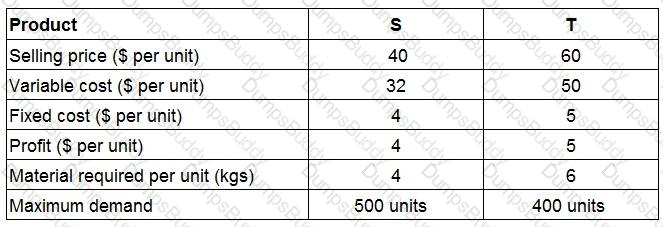
What is the optimal production plan?
EFG is a small business making raspberry jam to sell at local markets. It has recently been approached by a major supermarket to produce a special order for the supply of lemon curd.
Two of the ingredients required are sugar and preservatives, both of which are in inventory.
The sugar has a historic cost of $4 per kg and a replacement cost of $5. It is in regular use for the production of the raspberry jam.
The factory has switched to organic processes and the preservatives are no longer required.
The historic cost of the preservatives was $3 per kg and the replacement cost is $2.50 per kg.
The preservatives can be re-sold to a local competitor for $1 per kg if they are not used in this order.
Which TWO of the following should be included in determining the relevant cost of the special order?
A company makes a product using two materials, X and Y.
The standard materials required for one unit of the product are:

What is the materials yield variance?
Give your answer as a whole number.
When classifying quality costs, which of the following is NOT likely to be an appraisal cost?
200 units each of components F, G and H are required next period.
All three components are made by skilled labour of which only 4,000 hours are available.
An external supplier is able to supply any requirements of the components.
No inventories are held.
Data for the three components are as follows:

In order to minimise cost, how many units of component H should be purchased from the external supplier?
A company's initial budget for month 3 includes sales of $100,000, a contribution to sales (C/S) ratio of 40% and fixed costs of $20,000.
If the budgeted sales volume in month 3 is reduced by 5% but contribution per unit, total fixed costs and sales mix are unchanged, which of the following statements, about the change to the budgeted profit or contribution in month 3 is true?
Company Y absorbs fixed production overheads using a rate per machine hour. Budgeted and actual data for month 8 are as follows:
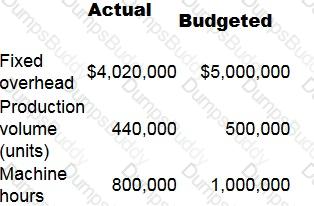
What is the fixed production overhead efficiency variance?
XY can choose from four mutually exclusive projects. The projects will each last for one year and their net cash inflows will be determined by market conditions. The forecast net cash inflows for each of the possible outcomes are shown below.

If the company applies the maximin criterion the project chosen would be:
A manager has to decide between four mutually exclusive projects, A, B, C and D:
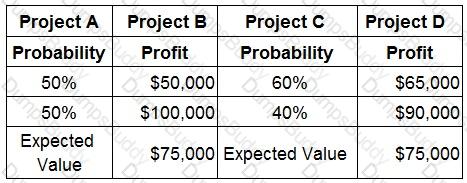
Using the above information, which Project would a risk seeking manager choose?
How would the cost of recycling scrap be classified in an environmental costing system?
Company M is preparing its budgeted profit statement for the next year.
The initial budget for Product A is as follows with some changes proposed by the sales director to increase the quality of the product.
What would the budgeted profit of Product A be if the proposed changes are made?
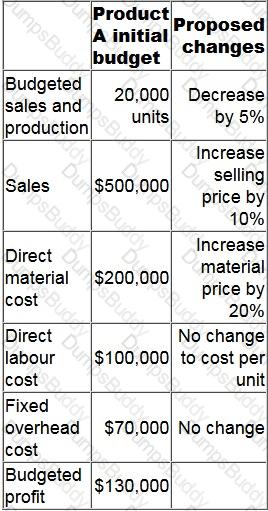
Give your answer as a whole number.
FGH used to manufacture components that required raw material Q.
Currently there are 80 kg of material Q in inventory.
The company has no use for the material in the foreseeable future and intends to sell it for scrap.
A potential new customer has asked for a price for a large order.
This order would require 100 kg of material Q.
The company management has decided to quote a price for this work on a relevant cost basis.
Details of costs for material Q are as follows:
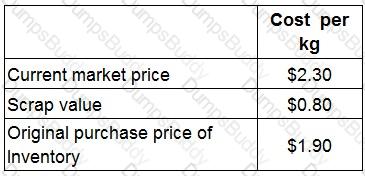
What would be the relevant cost of Material Q to use in this order?
Which of the following managers is most likely to be responsible for an favourable labour efficiency variance?
Which of the following are examples of feedforward control?
Select ALL that apply.
Product G has the following sales information:
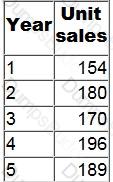
If moving averages of annual sales over 3-year periods are calculated, what is the moving average at Year 3?
Forecast sales demand of product W next period is 6,800 units. Product W requires 5 kg of material Y, seven hours of skilled labour and six hours of semi-skilled labour.
Availability of resources for next period is forecast as follows:
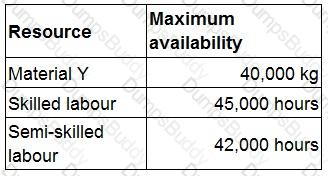
No inventories are held.
What is the principal budget factor for next period?
GP is launching a new product. The annual forecast costs are as follows:
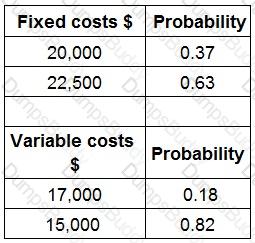
What is the expected value of the total costs?
Give your answer to the nearest whole $.
Which THREE of the following statements relating to fixed overhead variances are correct?
A company operates a customer complaints department.
How will the cost of the customer complaints department be classified in a system focussed on quality related costs?
A company manufactures a single product. The following budgeted data applies to month 6:
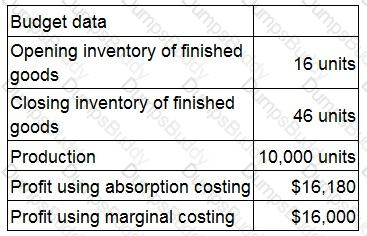
What was the budgeted fixed production overhead for month 6?
Give your answer to the nearest whole $ (in '000s).
Which of the statements about allocation of joint costs to products are true and which are false?
