What is true about API implementations when dealing with legal regulations that require all data processing to be performed within a certain jurisdiction (such as in the USA or the EU)?
In which layer of API-led connectivity, does the business logic orchestration reside?
Which layer in the API-led connectivity focuses on unlocking key systems, legacy systems, data sources etc and exposes the functionality?
A company uses a hybrid Anypoint Platform deployment model that combines the EU control plane with customer-hosted Mule runtimes. After successfully testing a Mule API implementation in the Staging environment, the Mule API implementation is set with environment-specific properties and must be promoted to the Production environment. What is a way that MuleSoft recommends to configure the Mule API implementation and automate its promotion to the Production environment?
A System API is designed to retrieve data from a backend system that has scalability challenges. What API policy can best safeguard the backend system?
Refer to the exhibit.
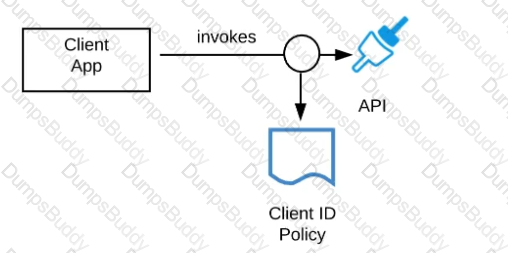
A developer is building a client application to invoke an API deployed to the STAGING environment that is governed by a client ID enforcement policy.
What is required to successfully invoke the API?
A Mule application exposes an HTTPS endpoint and is deployed to three CloudHub workers that do not use static IP addresses. The Mule application expects a high volume of client requests in short time periods. What is the most cost-effective infrastructure component that should be used to serve the high volume of client requests?
When designing an upstream API and its implementation, the development team has been advised to NOT set timeouts when invoking a downstream API, because that downstream API has no SLA that can be relied upon. This is the only downstream API dependency of that upstream API.
Assume the downstream API runs uninterrupted without crashing. What is the impact of this advice?
A system API is deployed to a primary environment as well as to a disaster recovery (DR) environment, with different DNS names in each environment. A process API is a client to the system API and is being rate limited by the system API, with different limits in each of the environments. The system API's DR environment provides only 20% of the rate limiting offered by the primary environment. What is the best API fault-tolerant invocation strategy to reduce overall errors in the process API, given these conditions and constraints?
An organization has several APIs that accept JSON data over HTTP POST. The APIs are all publicly available and are associated with several mobile applications and web applications.
The organization does NOT want to use any authentication or compliance policies for these APIs, but at the same time, is worried that some bad actor could send payloads that could somehow compromise the applications or servers running the API implementations.
What out-of-the-box Anypoint Platform policy can address exposure to this threat?
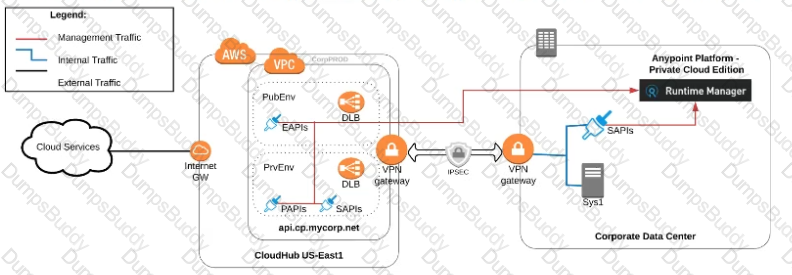
An organization uses various cloud-based SaaS systems and multiple on-premises systems. The on-premises systems are an important part of the organization's application network and can only be accessed from within the organization's intranet.
What is the best way to configure and use Anypoint Platform to support integrations with both the cloud-based SaaS systems and on-premises systems?
A) Use CloudHub-deployed Mule runtimes in an Anypoint VPC managed by Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition control plane
B)Use CloudHub-deployed Mule runtimes in the shared worker cloud managed by the MuleSoft-hosted Anypoint Platform control plane
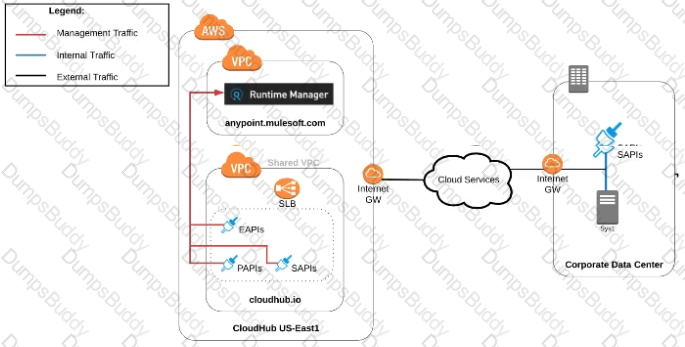
C)Use an on-premises installation of Mule runtimes that are completely isolated with NO external network access, managed by the Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition control plane
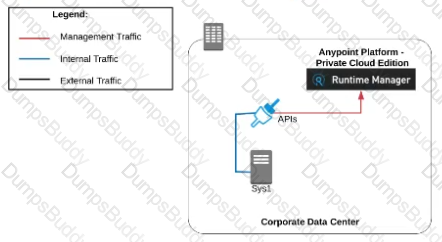
D)Use a combination of Cloud Hub-deployed and manually provisioned on-premises Mule runtimes managed by the MuleSoft-hosted Anypoint Platform control plane
An API client calls one method from an existing API implementation. The API implementation is later updated. What change to the API implementation would require the API client's invocation logic to also be updated?
An Order API must be designed that contains significant amounts of integration logic and involves the invocation of the Product API.
The power relationship between Order API and Product API is one of "Customer/Supplier", because the Product API is used heavily throughout the organization and is developed by a dedicated development team located in the office of the CTO.
What strategy should be used to deal with the API data model of the Product API within the Order API?
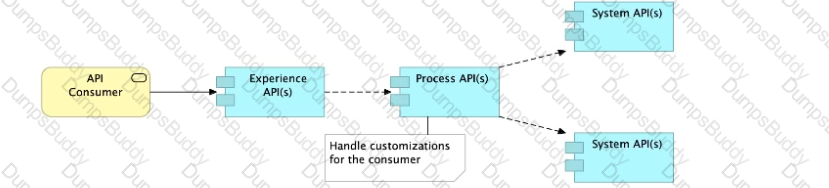
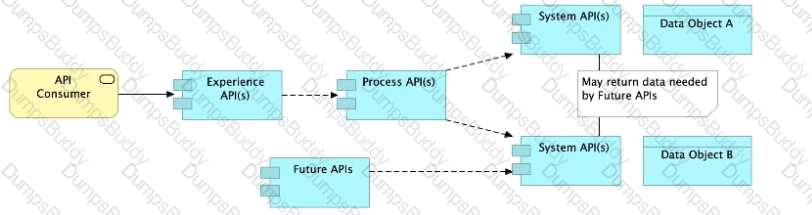
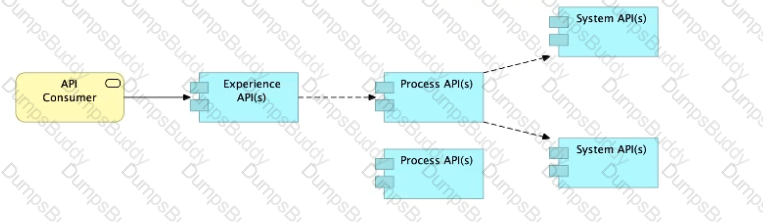
Refer to the exhibit.
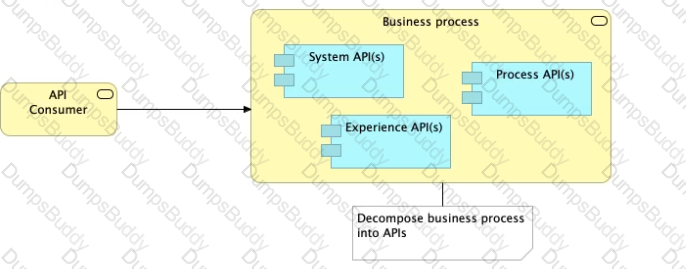
What is the best way to decompose one end-to-end business process into a collaboration of Experience, Process, and System APIs?
A) Handle customizations for the end-user application at the Process API level rather than the Experience API level
B)Allow System APIs to return data that is NOT currently required by the identified Process or Experience APIs
C)Always use a tiered approach by creating exactly one API for each of the 3 layers (Experience, Process and System APIs)

D)Use a Process API to orchestrate calls to multiple System APIs, but NOT to other Process APIs
A retail company is using an Order API to accept new orders. The Order API uses a JMS queue to submit orders to a backend order management service. The normal load for orders is being handled using two (2) CloudHub workers, each configured with 0.2 vCore. The CPU load of each CloudHub worker normally runs well below 70%. However, several times during the year the Order API gets four times (4x) the average number of orders. This causes the CloudHub worker CPU load to exceed 90% and the order submission time to exceed 30 seconds. The cause, however, is NOT the backend order management service, which still responds fast enough to meet the response SLA for the Order API. What is the MOST resource-efficient way to configure the Mule application's CloudHub deployment to help the company cope with this performance challenge?
An organization wants MuleSoft-hosted runtime plane features (such as HTTP load balancing, zero downtime, and horizontal and vertical scaling) in its Azure environment. What runtime plane minimizes the organization's effort to achieve these features?
A company requires Mule applications deployed to CloudHub to be isolated between non-production and production environments. This is so Mule applications deployed to non-production environments can only access backend systems running in their customer-hosted non-production environment, and so Mule applications deployed to production environments can only access backend systems running in their customer-hosted production environment. How does MuleSoft recommend modifying Mule applications, configuring environments, or changing infrastructure to support this type of per-environment isolation between Mule applications and backend systems?
Traffic is routed through an API proxy to an API implementation. The API proxy is managed by API Manager and the API implementation is deployed to a CloudHub VPC using Runtime Manager. API policies have been applied to this API. In this deployment scenario, at what point are the API policies enforced on incoming API client requests?
Mule applications that implement a number of REST APIs are deployed to their own subnet that is inaccessible from outside the organization.
External business-partners need to access these APIs, which are only allowed to be invoked from a separate subnet dedicated to partners - called Partner-subnet. This subnet is accessible from the public internet, which allows these external partners to reach it.
Anypoint Platform and Mule runtimes are already deployed in Partner-subnet. These Mule runtimes can already access the APIs.
What is the most resource-efficient solution to comply with these requirements, while having the least impact on other applications that are currently using the APIs?
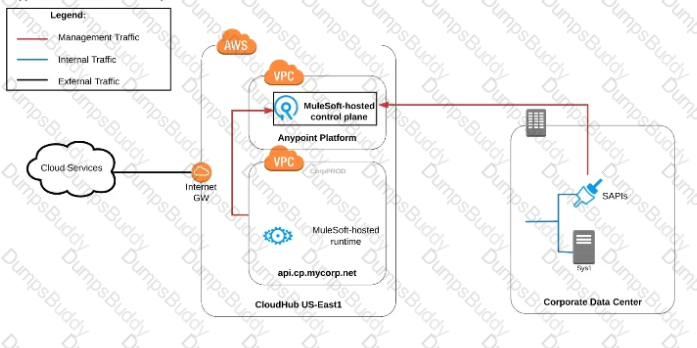
Refer to the exhibit.
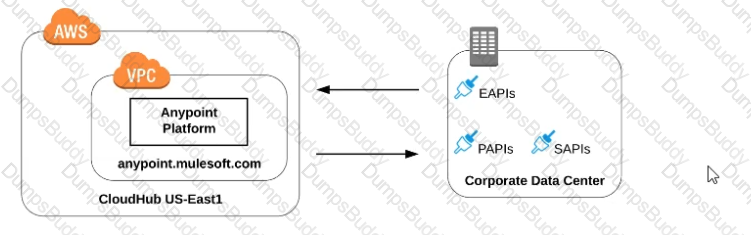
what is true when using customer-hosted Mule runtimes with the MuleSoft-hosted Anypoint Platform control plane (hybrid deployment)?
When could the API data model of a System API reasonably mimic the data model exposed by the corresponding backend system, with minimal improvements over the backend system's data model?
What best describes the Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs), also known as DNS entries, created when a Mule application is deployed to the CloudHub Shared Worker Cloud?