As the persistence parameter under GARCH is lowered, which of the following would be true:
Once the frequency and severity distributions for loss events have been determined, which of the following is an accurate description of the process to determine a full loss distribution for operational risk?
Which of the following are valid approaches for extreme value analysis given a dataset:
I. The Block Maxima approach
II. Least squares approach
III. Maximum likelihood approach
IV. Peak-over-thresholds approach
The systemic manifestation of the liquidity crisis during the current credit crisis took many forms. Which of the following is not one of those forms?
A bank's detailed portfolio data on positions held in a particular security across the bank does not agree with the aggregate total position for that security for the bank. What data quality attribute is missing in this situation?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. A transition matrix is the probability of a security migrating from one rating class to another during its lifetime.
II. Marginal default probabilities refer to probabilities of default in a particular period, given survival at the beginning of that period.
III. Marginal default probabilities will always be greater than the corresponding cumulative default probability.
IV. Loss given default is generally greater when recovery rates are low.
The results of 'desk-level' stress tests cannot be added together to arrive at institution wide estimates because:
Which loss event type is the loss of personally identifiable client information classified as under the Basel II framework?
Which of the following decisions need to be made as part of laying down a system for calculating VaR:
I. How returns are calculated, eg absoluted returns, log returns or relative/percentage returns
II. Whether VaR is calculated based on historical simulation, Monte Carlo, or is computed parametrically
III. Whether binary/digital options are included in the portfolio positions
IV. How volatility is estimated
The accuracy of a VaR estimate based on a Monte carlo simulation of portfolio prices is affected by:
I. The shape of the distribution of portfolio values
II. The number simulations carried out
III. The confidence level selected for the VaR estimate
According to the Basel II framework, subordinated term debt that was originally issued 4 years ago with a maturity of 6 years is considered a part of:
The sum of the stand alone economic capital of all the business units of a bank is:
A corporate bond maturing in 1 year yields 8.5% per year, while a similar treasury bond yields 4%. What is the probability of default for the corporate bond assuming the recovery rate is zero?
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Shocks to risk factors should be relative rather than absolute if we wish to avoid a change in the sign of the risk factor.
II. Interest rate shocks are generally modeled as absolute shocks.
III. Shocks to volatility are generally modeled as absolute shocks.
IV. Shocks to market spreads are generally modeled as relative shocks.
In January, a bank buys a basket of mortgages with a view to securitize them by April. Due to an unexpected lack of investors in the securitization market, it is unable to do so and is left with the exposure to the mortgages on its books. This is an example of:
Which of the following is not a parameter to be determined by the risk manager that affects the level of economic credit capital:
A Bank Holding Company (BHC) is invested in an investment bank and a retail bank. The BHC defaults for certain if either the investment bank or the retail bank defaults. However, the BHC can also default on its own without either the investment bank or the retail bank defaulting. The investment bank and the retail bank's defaults are independent of each other, with a probability of default of 0.05 each. The BHC's probability of default is 0.11.
What is the probability of default of both the BHC and the investment bank? What is the probability of the BHC's default provided both the investment bank and the retail bank survive?
Which of the following are valid criticisms of value at risk:
I. There are many risks that a VaR framework cannot model
II. VaR does not consider liquidity risk
III. VaR does not account for historical market movements
IV. VaR does not consider the risk of contagion
Under the CreditPortfolio View approach to credit risk modeling, which of the following best describes the conditional transition matrix:
Which of the following statements is true in relation to the Supervisory Capital Assessment Program (SCAP):
I. The SCAP is an annual exercise conducted by the Treasury Department to determine the health of key financial institutions in the US economy
II. The SCAP was essentially a stress test where the stress scenarios were specified by the regulators
III. Capital buffers calculated under the SCAP represented the amount of capital that the institutions covered by SCAP held in excess of Basel II requirements
IV. The SCAP focused on both total Tier 1 capital as well as Tier 1 common capital
Between two options positions with the same delta and based upon the same underlying, which would have a smaller VaR?
A bank expects the error rate in transaction data entry for a particular business process to be 0.005%. What is the range of expected errors in a day within +/- 2 standard deviations if there are 2,000,000 such transactions each day?
What is the 1-day VaR at the 99% confidence interval for a cash flow of $10m due in 6 months time? The risk free interest rate is 5% per annum and its annual volatility is 15%. Assume a 250 day year.
According to the implied capital model, operational risk capital is estimated as:
Which of the following statements are true:
I. A high score according to Altman's Z-Score methodology indicates a lower default risk
II. A high score according to the Probit or Logit models indicates a higher default risk
III. A high score according to Altman's Z-Score methodology indicates a higher default risk
IV. A high score according to the Probit or Logit models indicates a lower default risk
Ex-ante VaR estimates may differ from realized P&L due to:
I. the effect of intra day trading
II. timing differences in the accounting systems
III. incorrect estimation of VaR parameters
IV. security returns exhibiting mean reversion
According to the Basel framework, shareholders' equity and reserves are considered a part of:
Under the credit migration approach to assessing portfolio credit risk, which of the following are needed to generate a distribution of future portfolio values?
Which of the following statements are correct?
I. A reliance upon conditional probabilities and a-priori views of probabilities is called the 'frequentist' view
II. Knightian uncertainty refers to things that might happen but for which probabilities cannot be evaluated
III. Risk mitigation and risk elimination are approaches to reacting to identified risks
IV. Confidence accounting is a reference to the accounting frauds that were seen in the past decade as a reflection of failed governance processes
Which of the below are a way to classify risk governance structures:
A Reactive, Preventative and Active
B. Committee based, regulation based and board mandated
C. Top-down and Bottom-up
D. Active and Passive
A risk analyst uses the GARCH model to forecast volatility, and the parameters he uses are ω = 0.001%, α = 0.05 and β = 0.93. Yesterday's daily volatility was calculated to be 1%. What is the long term annual volatility under the analyst's model?
What would be the consequences of a model of economic risk capital calculation that weighs all loans equally regardless of the credit rating of the counterparty?
I. Create an incentive to lend to the riskiest borrowers
II. Create an incentive to lend to the safest borrowers
III. Overstate economic capital requirements
IV. Understate economic capital requirements
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Credit risk and counterparty risk are synonymous
II. Counterparty risk is the contingent risk from a counterparty's default in derivative transactions
III. Counterparty risk is the risk of a loan default or the risk from moneys lent directly
IV. The exposure at default is difficult to estimate for credit risk as it depends upon market movements
Which of the following statements are correct:
I. A training set is a set of data used to create a model, while a control set is a set of data is used to prove that the model actually works
II. Cleansing, aggregating or ensuring data integrity is a task for the IT department, and is not a risk manager's responsibility
III. Lack of information on the quality of underlying securities and assets was a major cause of the collapse in the CDO markets during the credit crisis that started in 2007
IV. The problem of lack of historical data can be addressed reasonably satisfactorily by using analytical approaches
Under the KMV Moody's approach to credit risk measurement, which of the following expressions describes the expected 'default point' value of assets at which the firm may be expected to default?
Which of the formulae below describes incremental VaR where a new position 'm' is added to the portfolio? (where p is the portfolio, and V_i is the value of the i-th asset in the portfolio. All other notation and symbols have their usual meaning.)
A)
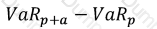
B)
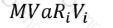
C)
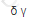
D)
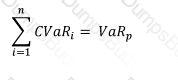
Which of the following was not a policy response introduced by Basel 2.5 in response to the global financial crisis:
Which of the following statements is true:
I. When averaging quantiles of two Pareto distributions, the quantiles of the averaged models are equal to the geometric average of the quantiles of the original models based upon the number of data items in each original model.
II. When modeling severity distributions, we can only use distributions which have fewer parameters than the number of datapoints we are modeling from.
III. If an internal loss data based model covers the same risks as a scenario based model, they can can be combined using the weighted average of their parameters.
IV If an internal loss model and a scenario based model address different risks, the models can be combined by taking their sums.
The minimum 'multiplication factor' to be applied to VaR calculations for calculating the capital requirements for the trading book per Basel II is equal to:
An equity manager holds a portfolio valued at $10m which has a beta of 1.1. He believes the market may see a dip in the coming weeks and wishes to eliminate his market exposure temporarily. Market index futures are available and the current futures notional on these is $50,000 per contract. Which of the following represents the best strategy for the manager to hedge his risk according to his views?
A risk analyst attempting to model the tail of a loss distribution using EVT divides the available dataset into blocks of data, and picks the maximum of each block as a data point to consider.
Which approach is the risk analyst using?
Which of the following are elements of 'group risk':
I. Market risk
II. Intra-group exposures
III. Reputational contagion
IV. Complex group structures
If A and B be two uncorrelated securities, VaR(A) and VaR(B) be their values-at-risk, then which of the following is true for a portfolio that includes A and B in any proportion. Assume the prices of A and B are log-normally distributed.