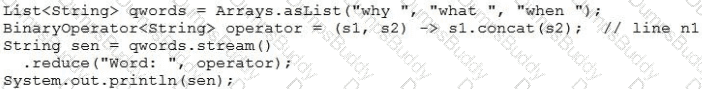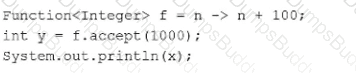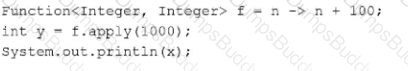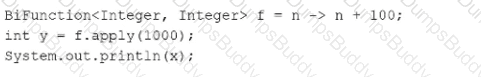1z0-809 Java SE 8 Programmer II Questions and Answers
Given the code fragments:
class MyThread implements Runnable {
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger (0);
public void run () {
int x = count.incrementAndGet();
System.out.print (x+” “);
}
}
and
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new MyThread());
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new MyThread());
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new MyThread());
Thread [] ta = {thread1, thread2, thread3};
for (int x= 0; x < 3; x++) {
ta[x].start();
}
Which statement is true?
Given the definition of the Emp class:
public class Emp
private String eName;
private Integer eAge;
Emp(String eN, Integer eA) {
this.eName = eN;
this.eAge = eA;
}
public Integer getEAge () {return eAge;}
public String getEName () {return eName;}
}
and code fragment:
List
Predicate
li = li.stream().filter(agVal).collect(Collectors.toList());
Stream
names.forEach(n -> System.out.print(n + “ “));
What is the result?
Given:
class UserException extends Exception { }
class AgeOutOfLimitException extends UserException { }
and the code fragment:
class App {
public void doRegister(String name, int age)
throws UserException, AgeOutOfLimitException {
if (name.length () < 6) {
throw new UserException ();
} else if (age >= 60) {
throw new AgeOutOfLimitException ();
} else {
System.out.println(“User is registered.”);
}
}
public static void main(String[ ] args) throws UserException {
App t = new App ();
t.doRegister(“Mathew”, 60);
}
}
What is the result?
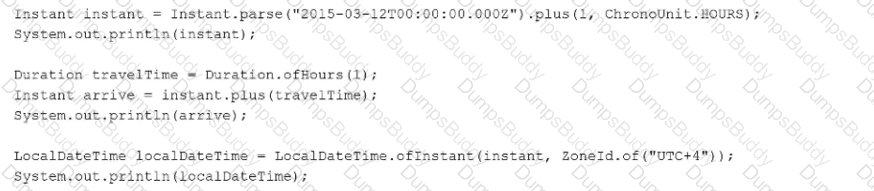
Given:

What change should you make to guarantee a single order of execution (printed values 1 -100 in order)?
Given the EMPLOYEE table;

Given the code fragment:

Assuming the database supports scrolling and updating, what is the result?
Given:

and the code fragment:

Assuming candlist contains Candidate objects, which code fragment calculates the average age of candidates from NewYork?
Given:
public class Canvas implements Drawable {
public void draw () { }
}
public abstract class Board extends Canvas { }
public class Paper extends Canvas {
protected void draw (int color) { }
}
public class Frame extends Canvas implements Drawable {
public void resize () { }
}
public interface Drawable {
public abstract void draw ();
}
Which statement is true?
Given the code fragment:
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader brCopy = null;
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new FileReader(“employee.txt”))) { //
line n1
br.lines().forEach(c -> System.out.println(c));
brCopy = br;//line n2
}
brCopy.ready(); //line n3;
}
Assume that the ready method of the BufferedReader, when called on a closed BufferedReader, throws an exception, and employee.txt is accessible and contains valid text.
What is the result?
Given the content of Operator.java, EngineOperator.java, and Engine.java files:

and the code fragment:
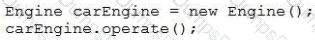
What is the result?
Given the code fragment:

Which should be inserted into line n1 to print Average = 2.5?
Given the code fragments:
class Caller implements Callable
String str;
public Caller (String s) {this.str=s;}
public String call()throws Exception { return str.concat (“Caller”);}
}
class Runner implements Runnable {
String str;
public Runner (String s) {this.str=s;}
public void run () { System.out.println (str.concat (“Runner”));}
}
and
public static void main (String[] args) InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future f1 = es.submit (new Caller (“Call”));
Future f2 = es.submit (new Runner (“Run”));
String str1 = (String) f1.get();
String str2 = (String) f2.get();//line n1
System.out.println(str1+ “:” + str2);
}
What is the result?
The data.doc, data.txt and data.xml files are accessible and contain text.
Given the code fragment:
Stream
Paths. get(“data.txt”),
Paths. get(“data.xml”));
paths.filter(s-> s.toString().endWith(“txt”)).forEach(
s -> {
try {
Files.readAllLines(s)
.stream()
.forEach(System.out::println); //line n1
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(“Exception”);
}
}
);
What is the result?
Given the code fragments:
class Employee {
Optional
address;Employee (Optional
address) {this.address = address;
}
public Optional
getAddress() { return address; }}
class Address {
String city = “New York”;
public String getCity { return city: }
public String toString() {
return city;
}
}
and
Address address = new Address;
Optional
addrs1 = Optional.ofNullable (address);Employee e1 = new Employee (addrs1);
String eAddress = (addrs1.isPresent()) ? addrs1.get().getCity() : “City Not
available”;
System.out.println(eAddress);
What is the result?
Given the code fragment:
LocalDate valentinesDay =LocalDate.of(2015, Month.FEBRUARY, 14);
LocalDate nextYear = valentinesDay.plusYears(1);
nextYear.plusDays(15); //line n1
System.out.println(nextYear);
What is the result?
Given the code fragments:
interface CourseFilter extends Predicate
public default boolean test (String str) {
return str.contains (“Java”);
}
}
and
List
Predicate
Predicate cf2 = new CourseFilter() { //line n1
public boolean test (String s) {
return s.startsWith (“Java”);
}
};
long c = strs.stream()
.filter(cf1)
.filter(cf2//line n2
.count();
System.out.println(c);
What is the result?
In 2015, daylight saving time in New York, USA, begins on March 8th at 2:00 AM. As a result, 2:00 AM becomes 3:00 AM.
Given the code fragment:

Which is the result?
Given the code fragment:

Assume that dbURL, userName, and password are valid.
Which code fragment can be inserted at line n1 to enable the code to print Connection Established?
Given:
class CheckClass {
public static int checkValue (String s1, String s2) {
return s1 length() – s2.length();
}
}
and the code fragment:
String[] strArray = new String [] {“Tiger”, “Rat”, “Cat”, “Lion”}
//line n1
for (String s : strArray) {
System.out.print (s + “ “);
}
Which code fragment should be inserted at line n1 to enable the code to print Rat Cat Lion Tiger?
Given the code fragment:
public void recDelete (String dirName) throws IOException {
File [ ] listOfFiles = new File (dirName) .listFiles();
if (listOfFiles ! = null && listOfFiles.length >0) {
for (File aFile : listOfFiles) {
if (aFile.isDirectory ()) {
recDelete (aFile.getAbsolutePath ());
} else {
if (aFile.getName ().endsWith (“.class”))
aFile.delete ();
}
}
}
}
Assume that Projects contains subdirectories that contain .class files and is passed as an argument to the recDelete () method when it is invoked.
What is the result?
Given:

and the code fragment:

Which modification enables the code fragment to print Speaker?
Given:

and the code fragment:

Which two code fragments, when inserted at line n1 independently, enable the code to print TruckCarBike?
Given:
class Sum extends RecursiveAction { //line n1
static final int THRESHOLD_SIZE = 3;
int stIndex, lstIndex;
int [ ] data;
public Sum (int [ ]data, int start, int end) {
this.data = data;
this stIndex = start;
this. lstIndex = end;
}
protected void compute ( ) {
int sum = 0;
if (lstIndex – stIndex <= THRESHOLD_SIZE) {
for (int i = stIndex; i < lstIndex; i++) {
sum += data [i];
}
System.out.println(sum);
} else {
new Sum (data, stIndex + THRESHOLD_SIZE, lstIndex).fork( );
new Sum (data, stIndex,
Math.min (lstIndex, stIndex + THRESHOLD_SIZE)
).compute ();
}
}
}
and the code fragment:
ForkJoinPool fjPool = new ForkJoinPool ( );
int data [ ] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
fjPool.invoke (new Sum (data, 0, data.length));
and given that the sum of all integers from 1 to 10 is 55.
Which statement is true?
Given:
Book.java:
public class Book {
private String read(String bname) { return “Read” + bname }
}
EBook.java:
public class EBook extends Book {
public class String read (String url) { return “View” + url }
}
Test.java:
public class Test {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Book b1 = new Book();
b1.read(“Java Programing”);
Book b2 = new EBook();
b2.read(“http://ebook.com/ebook”);
}
}
What is the result?
Which statement is true about the single abstract method of the java.util.function.Predicate interface?
Given:
class Student {
String course, name, city;
public Student (String name, String course, String city) {
this.course = course; this.name = name; this.city = city;
}
public String toString() {
return course + “:” + name + “:” + city;
}
public String getCourse() {return course;}
public String getName() {return name;}
public String getCity() {return city;}
and the code fragment:
List
new Student (“Jessy”, “Java ME”, “Chicago”),
new Student (“Helen”, “Java EE”, “Houston”),
new Student (“Mark”, “Java ME”, “Chicago”));
stds.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getCourse))
.forEach(src, res) -> System.out.println(scr));
What is the result?
Given:
class Vehicle implements Comparable
int vno;
String name;
public Vehicle (int vno, String name) {
this.vno = vno,;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString () {
return vno + “:” + name;
}
public int compareTo(Vehicle o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.name);
}
and this code fragment:
Set
vehicles.add(new Vehicle (10123, “Ford”));
vehicles.add(new Vehicle (10124, “BMW”));
System.out.println(vehicles);
What is the result?
Given the code fragment:
List
DoubleFunction funD = d –> d + 100.0;
doubles.stream (). forEach (funD); // line n1
doubles.stream(). forEach(e –> System.out.println(e)); // line n2
What is the result?
Given:
class Vehicle {
int vno;
String name;
public Vehicle (int vno, String name) {
this.vno = vno,;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString () {
return vno + “:” + name;
}
}
and this code fragment:
Set
vehicles.add(new Vehicle (10123, “Ford”));
vehicles.add(new Vehicle (10124, “BMW”));
System.out.println(vehicles);
What is the result?
Which two methods from the java.util.stream.Stream interface perform a reduction operation? (Choose two.)
Given:
public class Test
private T t;
public T get () {
return t;
}
public void set (T t) {
this.t = t;
}
public static void main (String args [ ] ) {
Test
Test type 1 = new Test ();//line n1
type.set(“Java”);
type1.set(100);//line n2
System.out.print(type.get() + “ “ + type1.get());
}
}
What is the result?
Given the code fragment:
List
System.out.println (
// line n1
);
Which code fragment, when inserted at line n1, enables the code to print the count of string elements whose length is greater than three?
Given the code fragment:
List
codes.forEach (c -> System.out.print(c + “ “));
String fmt = codes.stream()
.filter (s-> s.contains (“PEG”))
.reduce((s, t) -> s + t).get();
System.out.println(“\n” + fmt);
What is the result?
Given the code fragment:
public void recDelete (String dirName) throws IOException {
File [ ] listOfFiles = new File (dirName) .listFiles();
if (listOfFiles ! = null && listOfFiles.length >0) {
for (File aFile : listOfFiles) {
if (!aFile.isDirectory ()) {
if (aFile.getName ().endsWith (“.class”))
aFile.delete ();
}
}
}
}
Assume that Projects contains subdirectories that contain .class files and is passed as an argument to the recDelete () method when it is invoked.
What is the result?
Given the code fragments:
class TechName {
String techName;
TechName (String techName) {
this.techName=techName;
}
}
and
List
new TechName(“Java-“),
new TechName(“Oracle DB-“),
new TechName(“J2EE-“)
);
Stream
//line n1
Which should be inserted at line n1 to print Java-Oracle DB-J2EE-?
Given the structure of the EHF and DEPT tables:
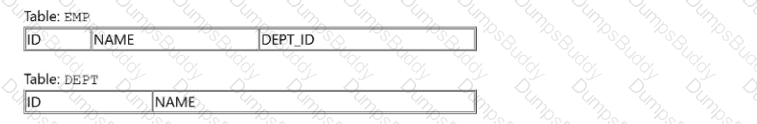
Given the code fragment:

What is the result?
Given that these files exist and are accessible:
/sports/info.txt
/sports/cricket/players.txt
/sports/cricket/data/ODI.txt
and given the code fragment:
int maxDepth =2;
Stream
maxDepth,
(p, a) -> p.getFileName().toString().endsWith (“txt”),
FileVisitOption.FOLLOW_LINKS);
Long fCount = paths.count();
System.out.println(fCount);
Assuming that there are NO soft-link/symbolic links to any of the files in the directory structure, what is the result?
Given the code fragment:
List
List
//line n1
Which code fragment, when inserted at line n1, prints 10 20 15 30?
Given this code;

Which two are correct after this class is instantiated and tested?
Given that version.txt is accessible and contains:
1234567890
and given the code fragment:

What is the result?
Given the code fragment:

Which code fragment, when inserted at line n1, ensures false is printed?